It's a condition that affects a woman of children bearing age’s hormone levels. Women with PCOS produce higher than normal amounts of male hormones. The hormonal imbalance causes their body to skip menstrual periods and makes it harder for them to get pregnant.
PCOS also causes hair growth on the face and body, and baldness. And it can contribute to long-term health problems like diabetes and heart diseases. Birth control pills and diabetes drugs (which combat insulin resistance, a PCOS symptom) can help fix the hormone imbalance and improve symptoms.
Many women have PCOS but don’t know it. PCOS affects a woman’s ovaries, the reproductive organs that produce estrogen and progesterone hormones that regulate the menstrual cycle. The ovaries also produce a small amount of male hormones called androgens.
PCOS is a “syndrome,†or group of symptoms that affects the ovaries and ovulation. Its three main features are:
- cysts in the ovaries
- high levels of male hormones
- irregular or skipped periods
In PCOS, many small, fluid-filled sacs grow inside the ovaries. The word “polycystic†means “many cysts.†These sacs are actually follicles, each one containing an immature egg. The eggs never mature enough to trigger ovulation. Extra male hormones disrupt the menstrual cycle, so women with PCOS get fewer periods than usual.
WHAT CAUSES PCOS?
Doctors don’t know exactly what causes PCOS. They believe that high levels of male hormones prevent the ovaries from producing hormones and making eggs normally. Genes, insulin resistance, and inflammation have all been linked to excess androgen( male hormone) production.
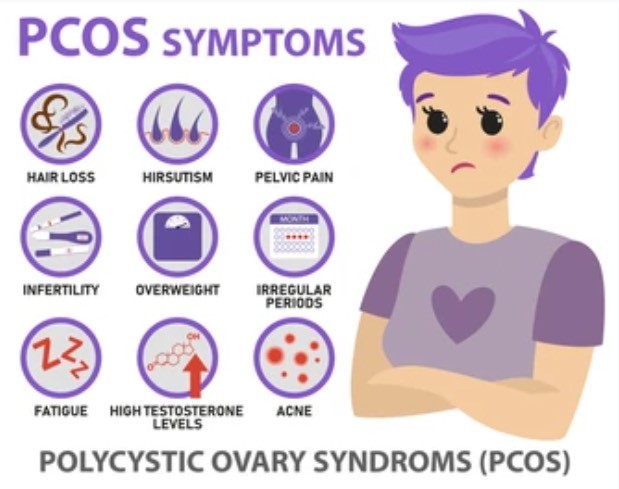
COMMON SYMPTOMS OF PCOS
Some women start seeing symptoms around the time of their first period. Others only discover they have PCOS after they’ve gained a lot of weight or they’ve had trouble getting pregnant. The most common PCOS symptoms are:
- Irregular periods: A lack of ovulation prevents the uterine lining from shedding every month. Some women with PCOS get fewer than eight periods a year or none at all
- Heavy bleeding: The uterine lining builds up for a longer period of time, so the periods you do get can be heavier than normal. Hair growth. More than 70% of women with this condition grow hair on their face and body; including on their back, belly, and chest. Excessive hair growth is called hirsutism.
- Acne: Male hormones can make the skin oilier than usual and cause breakouts on areas like the face, chest, and upper back.
- Weight gain: Up to 80% of women with PCOS are overweight or have obesity Darkening of the skin. Dark patches on the skin can form in body creases like those on the neck, in the groin, and under the breasts. Headaches. Hormone changes can trigger headaches in some women.
WHEN TO SEE THE DOCTOR
- You’ve had missed periods, and you’re not pregnant.
- You have symptoms of PCOS, such as hair growth on your face and body.
- You’ve been trying to get pregnant and you’ve not been successful.
- You have symptoms of diabetes, such as excess thirst or hunger, blurred vision, or unexplained weight loss.